Effects of realistic reradiation models in digital reconfigurable intelligent surfaces
Abstract
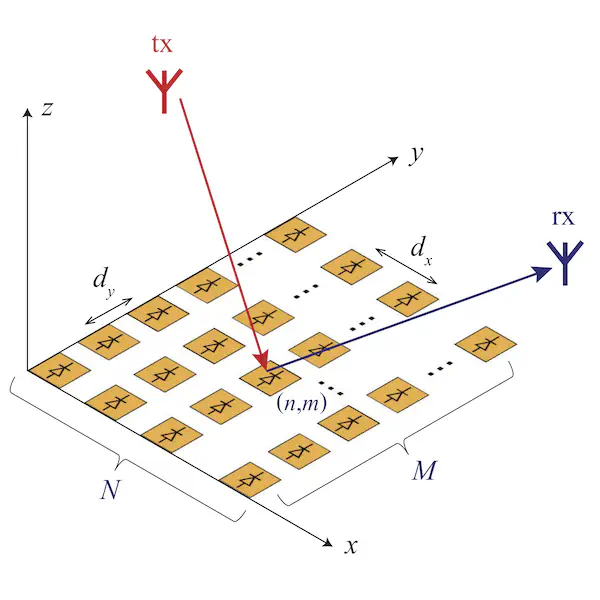
Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) are a promising technology for wireless communication applications, but their performance is often optimized using simplified electromagnetic reradiation models. In this study, we explore the impact on the RIS performance of more realistic assumptions, including the (possibly imperfect) quantization of the reflection coefficients, sub-wavelength inter-element spacing, near-field location, and presence of electromagnetic interference. We find that design constraints can cause an RIS to reradiate power in unwanted directions. Therefore, it is important to optimize an RIS by considering the entire reradiation pattern. Overall, our study indicates that a 2-bit digitally controllable RIS with a nearly constant reflection amplitude and RIS elements with a size and inter-element spacing between (1/8)th and (1/4)th of the signal wavelength may offer a reasonable tradeoff between performance, complexity, and cost.